Image Redaction
Overview
The Image Redaction API is used to automatically hide unwanted content in images. Using our automated APIs, you can define the types of content that need to be hidden such as explicit/illegal content or personal content.
This API is similar to the Image Moderation API, except that in addition to detecting unwanted content, the Image Redaction API will go one step further and return an updated version of the image where any unwanted content will have been hidden.
Below is an example of the redaction API configured to hide faces of children under 18:
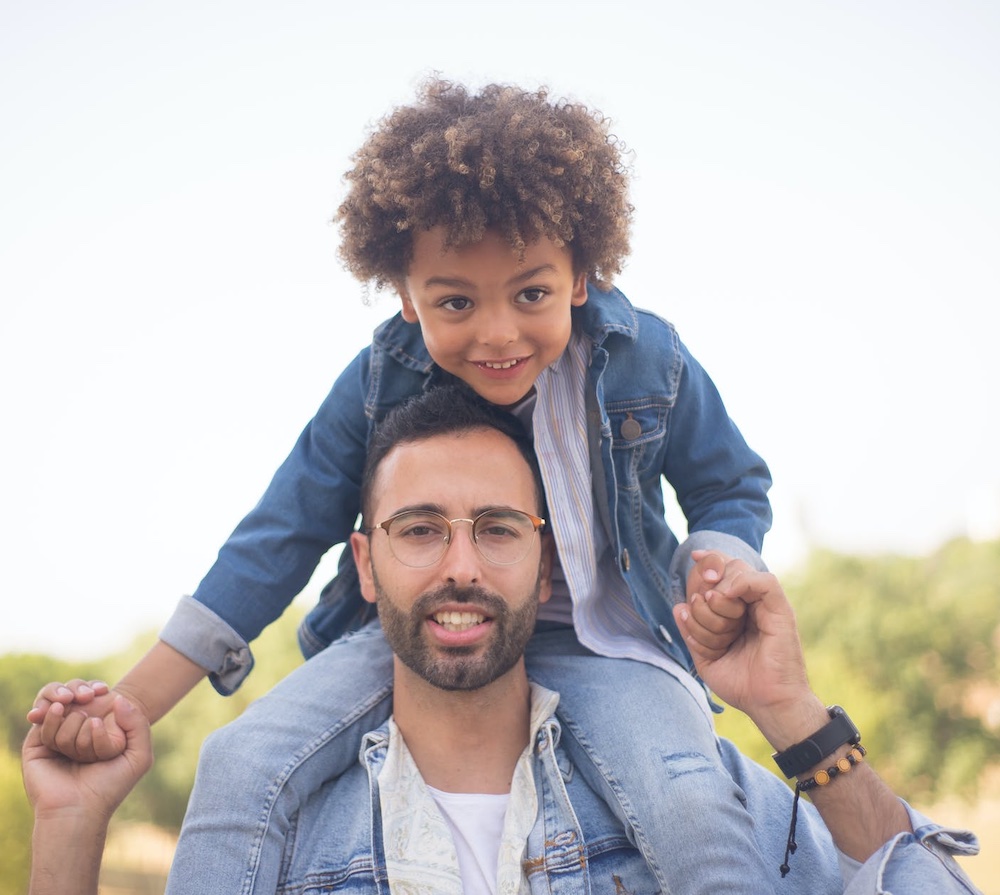
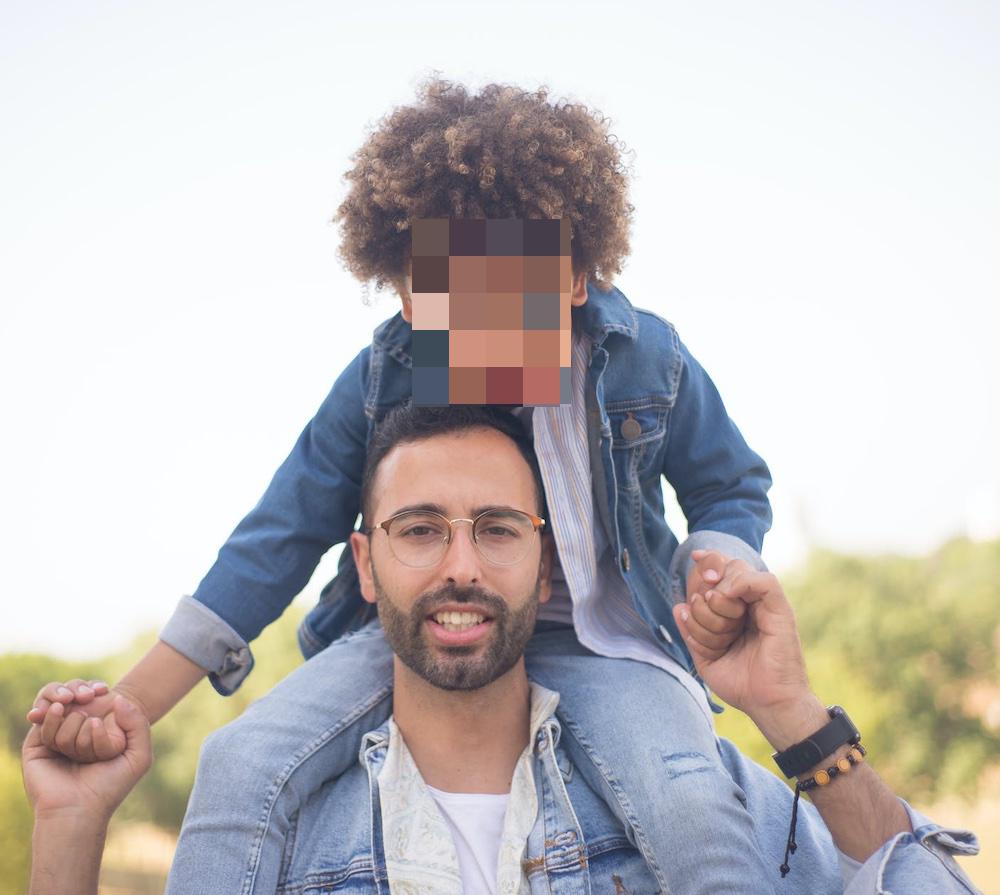


Get API access credentials
The Sightengine API uses a key pair that consists of an API user id and an API secret for authentication. To get your own API credentials, create an account and go the the API key page to retrieve them.
Image Redaction concepts
The following concepts can be detected and hidden with the Image Redaction API. You can select any combination of the following concepts to customize the results you get.
| nudity | Hide all types of nudity from explicit to suggestive |
| nudity-raw | Hide raw nudity only: sexual activity, sexual display and erotica |
| - | |
| face | Hide all faces |
| face-minor | Hide faces of children under 18 |
| - | |
| license-plate | Hide license plates |
| - | |
| offensive | Hide offensive signs and gestures |
| - | |
| weapon | Hide weapons such as guns and rifles |
| alcohol | Hide alcoholic bevereages |
| recreational-drug | Hide recreational drugs such as joints, cannabis |
| medical-drug | Hide medical drugs |
| - | |
| gore | Hide gore and horrific imagery |
| - | |
| text-natural | Hide naturally occurring text |
| text-embedded | Hide embedded text |
| - | |
| profanity | Hide written profanity: insults, racial slurs, inappropriate language |
| link | Hide embedded URLs and links |
Hide embedded email addresses | |
| phone | Hide embedded phone numbers |
| social | Hide social network accounts and mentions |
| - | |
| qr | Hide QR codes |
| - |
Other custom concepts are available upon request. Feel free to reach out if you have specific needs.
Transform method
By default, the engine will pixelate any unwanted areas of the image. Other methods are available:
| Method | Description | Availability |
| Pixelation | Unwanted areas are hidden by pixelating the image with large square blocks, such as large pixels. This is usually the recommended approach. | Enabled by default |
| Masking | Unwanted areas are hidden with a uniform box. The box is typically black but other colors are possible. This is the most robust approach for anonymization. | Available upon request |
| Blurring | Unwanted areas are hidden through blurring. | Available upon request |
Code examples
Submit images
Let's say you want to hide nudity, child faces, email addresses and phone numbers that may be embedded in images. You will be using the following concepts: nudity, face-minor email and phone.
curl -X POST 'https://api.sightengine.com/1.0/transform.json' \
-F 'media=@./image1.jpg' \
-F 'concepts=nudity,face-minor,email,phone' \
-F 'api_user={api_user}' \
-F 'api_secret={api_secret}'
# this example uses requests
import requests
import json
params = {
'concepts': 'nudity,face-minor,email,phone',
'api_user': '{api_user}',
'api_secret': '{api_secret}'
}
files = {'media': open('./image1.jpg', 'rb')}
r = requests.post('https://api.sightengine.com/1.0/transform.json', files=files, data=params)
output = json.loads(r.text)
$params = array(
'media' => new CurlFile('./image1.jpg'),
'concepts' => 'nudity,face-minor,email,phone',
'api_user' => '{api_user}',
'api_secret' => '{api_secret}',
);
// this example uses cURL
$ch = curl_init('https://api.sightengine.com/1.0/transform.json');
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $params);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$output = json_decode($response, true);
// this example uses axios and form-data
const axios = require('axios');
const FormData = require('form-data');
const fs = require('fs');
data = new FormData();
data.append('media', fs.createReadStream('./image1.jpg'));
data.append('concepts', 'nudity,face-minor,email,phone');
data.append('api_user', '{api_user}');
data.append('api_secret', '{api_secret}');
axios({
method: 'post',
url:'https://api.sightengine.com/1.0/transform.json',
data: data,
headers: data.getHeaders()
})
.then(function (response) {
// on success: handle response
console.log(response.data);
})
.catch(function (error) {
// handle error
if (error.response) console.log(error.response.data);
else console.log(error.message);
});
The API will then return a JSON response. The response contains the base64 encoded image in the base64 field, along with the MIME type of the returned image in content-type.
{
"status": "success",
"request": {
"id": "req_56JCYHWOIpuU8dpmxeAKw",
"timestamp": 1513479454.157561,
"operations": 1
},
"transform": {
"content-type": "image/jpeg",
"base64": "/9j/4SFSdkZJRgAKa5B60Sk4PNKxwTUMZLhDgA5Jp5sLx7yC4FQ22hXjksxarH9iupw5JJ6ZjErgy5BFcSk..."
},
"media": {
"id": "med_56JCMAeruaoeSk4PdAqjf",
"uri": "image1.jpg"
}
}
Was this page helpful?